What is CDN?
CDN stands for content delivery network or content distribution network. A CDN is a globally distributed network of proxy servers deployed in multiple data centers. The goal of a CDN is to serve content to end-users with high availability and high performance. CDNs serve a large fraction of the Internet content today, including web objects (text, graphics and scripts), downloadable objects (media files, software, documents), applications (e-commerce, portals), live streaming media, on-demand streaming media, and social networks.
Operation
Most CDNs are operated as an ASP on the Internet (also known as on-demand software or software as a service (SaaS)). An increasing number of Internet network owners have built their own CDNs to improve on-net content delivery, reduce demand on their own telecommunications infrastructure, and to generate revenues from content customers. This might include offering access to media streaming to Internet service subscribers. Some larger software companies such as Microsoft build their own CDNs in tandem with their own products. Examples include Microsoft Azure CDN, Amazon CloudFront, and Google Cloud CDN.
Here content (potentially multiple copies) may exist on several servers. When a user makes a request to a CDN hostname, DNS will resolve to an optimized server (based on location, availability, cost, and other metrics) and that server will handle the request.
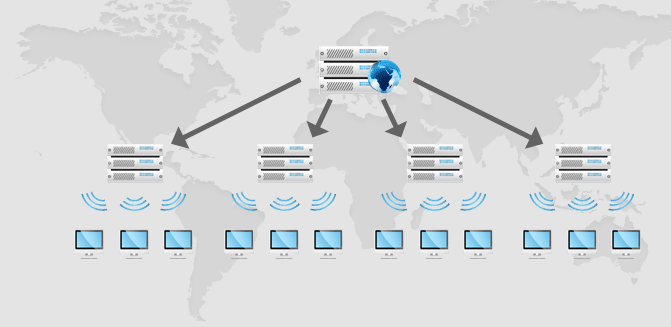
Technology
CDN nodes are usually deployed in multiple locations, often over multiple backbones. Benefits include reducing bandwidth costs, improving page load times, or increasing global availability of content. The number of nodes and servers making up a CDN varies, depending on the architecture, some reaching thousands of nodes with tens of thousands of servers on many remote points of presence (PoPs). Others build a global network and have a small number of geographical PoPs.
Requests for content are typically algorithmically directed to nodes that are optimal in some way. When optimizing for performance, locations that are best for serving content to the user may be chosen. This may be measured by choosing locations that are the fewest hops, the least number of network seconds away from the requesting client, or the highest availability in terms of server performance (both current and historical), so as to optimize delivery across local networks. When optimizing for cost, locations that are least expensive may be chosen instead. In an optimal scenario, these two goals tend to align, as ‘edge servers’ that are close to the end-user at the edge of the network may have an advantage in performance or cost.
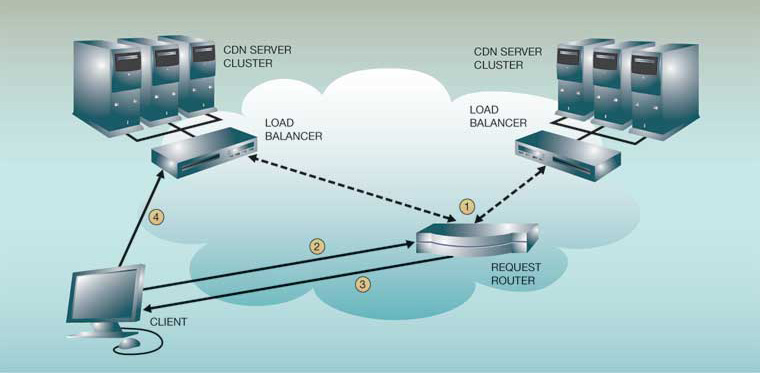
Most CDN providers will provide their services over a varying, defined, set of PoPs, depending on the geographic coverage desired, such as United States, International or Global, Asia-Pacific, etc. These sets of PoPs can be called “edges”, “edge nodes” or “edge networks” as they would be the closest edge of CDN assets to the end user.
The CDN’s Edge Network grows outward from the origin/s through further acquisitions (via purchase, peering, or exchange) of co-locations facilities, bandwidth, and servers.
source: Wikipedia