Metadata
When Search Boost indexes documents to make them searchable it reads the filename and the document content and uses this to build an index (set a title, a description, a URL for the result, etc). But there are times when you need to override these parameters.
To accomplish this you need to create metadata which are XML files that sit next to each document. The metadata file must be named exactly as the document but appended with the extension “.metadata” or “.sbmetadata”. For example, if the document is test.pdf, then the metadata file is test.pdf.metadata or test.pdf.sbmetadata.
Below is an example of a metadata file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<metadata>
<title>Friendly Document Title</title>
<titleToken>Some:Token</titleToken>
<desc>Some <b>description that comes from metadata document</b></desc>
<keywords>other important words not present in document</keywords>
<boost>16.0</boost>
<overrideUrl>//somesite.com/resultpage.html</overrideUrl>
<locale>en-US</locale>
<linkToTabId>123</linkToTabId>
<categories>
<cat>A Root Category</cat>
<cat>Another Root Category/Subcategory Name</cat>
</categories>
<data>
<item id="MyCustomField1">My custom value</item>
<item id="MyCustomField2">Other custom value</item>
</data>
<ignoreSecurity>true</ignoreSecurity>
</metadata>
All fields are optional. If not specified, they behave same as when the metadata file is not specified.
Here is a short explanation of the metadata fields:
- title
Normally, Search Boost uses the file name to display as title in the search results. Specify another text here to instruct Search Boost to use this instead. Search Boost integrates with My Tokens here so it can fetch the title of the document from a different data source, for example from the DNN documents module. Just create a database token in My Tokens. You will receive 2 parameters TknParams: Name and RelativePath. So this is the same as invoking token [Some:Token(Name=’mydoc’,RelativePath=’/mydoc.pdf’, FileName=’mydoc.pdf’)]
- desc
If not specified, Search Boost builds this from content. Supports My Tokens.
-
keywords If the document doesn’t contain some terms that you know are important in order to have the document better match the searches, then input additional keywords in this field. Supports My Tokens.
-
boost
Use this field to control how important the current document is. The more important a document is the higher it appears in search results.
- overrideUrl
When the search result is clicked the browser redirects to view/download the indexed document. However, sometimes you need the browser to redirect somewhere else where the click is handled. Use this field to specify that other URL. Supports My Tokens.
- locale
This is the locale code (for example en-US) that matches the content. Search Boost uses this setting to filter results based on current locale. Best strategy is to create sub folders for each locale, and create a per folder metadata file that sets the locale for the whole folder.
- linkToTabId
This is the locale code (for example en-US) that matches the content. Search Boost uses this setting to filter results based on current locale. Best strategy is to create sub folders for each locale, and create a per folder metadata file that sets the locale for the whole folder.
- categories (new in 2.5)
Use this field to attach any number of categories to a document. Categories are used for Faceted Search.
- data (new in 2.7)
This field allows attaching custom data to documents. These fields will be passed to the XSL template but also you can build custom filters.
- ignoreSecurity (new in 2.8.31)
When set to true, Search Boost will bring the results in the search results regardless of the security. But, if the user doesn’t have access to the file, the browser will redirect to the login page before redirecting to the file. Here is a video with a simple setup that uses the Ignore Security option youtu.be/Jov0OxzkWrM
- roles, deniedRoles, allowedUsers, deniedUsers (new in 5.0.103)
Security features can be implemented in the metadata file, according with the DNN standard. Nodes can be added with the following keys:
-
‘roles’ and ‘deniedRoles’ in which you specify the role names.
-
‘allowedUsers’ and ‘deniedUsers’ in which you specify the User Ids.
You can add items in these nodes in a list format, separating each item with “\n”, “;”, “,”.
Along with all the settings present in the admin console, metadata is a very powerful tool to fine tune searching. Also, metadata makes it very powerful to integrate with other document management software as long as there’s a “glue” application capable of reading the setting from the document management software and creating the metadata file. Important!
Make sure your encoding is UTF8. For example, in Notepad++, set it like this:
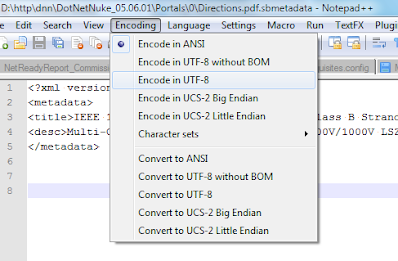
Also encode special characters such as
- & to &
- < to <
-
to >
These are all constraints imposed by the XML standard and the .NET implementation.
Per Folder Metadata
Starting with version 2.5 it’s possible to specify a metadata XML per folder. This means it will be applied to all documents in that folder. The file should be named .sbmetadata and it has the same structure as the per document XML except the title node.
Search Boost loads metadata in following order:
-
First, it initializes a metadata object with defaults based on file name, file contents, etc.
-
If a folder metadata file exists, it’s merged with current metadata; this means that only fields that exist in the folder metadata are copied to the document metadata. Categories are appended to existing set.
-
If document metadata file exists, it’s merged with current metadata using same rules as described at point 2.
This feature is very powerful to enable Faceted Search for documents, boost documents in a folder, or give some additional content to all documents in that folder.